 Automation has been deployed in telecom networks for decades, mainly for isolated operational cost reductions. The advent of 5G has dramatically changed the nature of automation and its adoption trends within the industry. Communication service providers (CSPs) are increasingly adopting automation powered by artificial intelligence (AI) to automate rules-based, high-volume tasks for the front and back end of their networks. By leveraging the capability of intelligent automation, CSPs can significantly reduce their operational costs, lower the time-to-market for introducing new products and services, and increase resource efficiency, ultimately improving overall customer experience and driving monetisation and growth.
Automation has been deployed in telecom networks for decades, mainly for isolated operational cost reductions. The advent of 5G has dramatically changed the nature of automation and its adoption trends within the industry. Communication service providers (CSPs) are increasingly adopting automation powered by artificial intelligence (AI) to automate rules-based, high-volume tasks for the front and back end of their networks. By leveraging the capability of intelligent automation, CSPs can significantly reduce their operational costs, lower the time-to-market for introducing new products and services, and increase resource efficiency, ultimately improving overall customer experience and driving monetisation and growth.
A look at the synergistic relationship between 5G and intelligent automation, global adoption trends, key deployments by telcos and future outlook…
Symbiosis of 5G and automation
5G and network automation have a symbiotic and interdependent relationship. AI-enabled automation serves as the backbone for the rapid deployment and configuration of 5G networks and its components such as small cells, millimetre wave frequencies, and massive MIMO arrays. In turn, the advanced capabilities of 5G provide the technological framework and platform for intelligent automation.
The intricate infrastructure of 5G networks makes manual configuration more complex and error-prone. The potential for human errors is minimised by automating routine tasks such as device provisioning, software updates and network monitoring. AI-enabled automation enables network operators to dynamically allocate resources, configure devices and manage traffic patterns, thereby optimising the performance of the 5G networks. It also facilitates consistent and standardised security across the network, ensuring the uniform application and monitoring of security measures.
Meanwhile, automation leverages AI, machine learning (ML) and data analytics supported by 5G to enhance network intelligence. The low latency of 5G allows real-time monitoring, control of network elements and equipment, and remote operation. This is critical for tasks such as software upgrades, troubleshooting and maintenance of networks. The increased data throughput of 5G also supports advanced analytics and ML algorithms to gain deeper insights into network performance.
Global adoption trends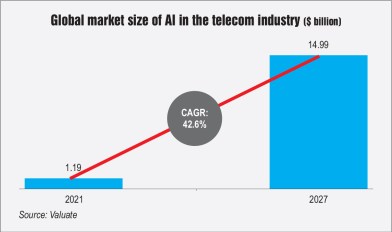
As telcos continue their global roll-out of 5G networks, they are increasingly prioritising the incorporation of automation and AI into their business strategies. While rules-based automation has been around for decades and is well-embedded into network processes, AI is currently at a more nascent stage, with the majority of implementations in small pockets or proofs of concept (PoCs). According to the International Data Corporation, 63.5 per cent of telcos are actively implementing AI to enhance their network infrastructure. The key application areas include network operations, base station site planning, truck-routing optimisation and ML data analytics. To improve customer experience, some telcos are adopting recommendation engines, virtual assistants and digital avatars. According to a study conducted by VMware, Inc. on the automation progress in the telecom industry, 70 per cent of the respondents contend that CSPs either have a solution or are planning to trial or deploy one. Several CSPs have reached a stage of network maturity where automation becomes a viable option for creating new LTE/5G service opportunities for their customers. The survey shows that the top drivers for investing in automation include reduction of operating expenses and acceleration of pathways to revenue generation.
However, a recent study by NVIDIA Corporation reveals that in an industry with a multi-billion capex spend per annum, the level of investment in AI has been relatively low. Reportedly, 50 per cent of respondents spent less than $1 million on AI. This shows that the industry’s level of investment in AI does not match its level of enthusiasm and engagement. This could be due to a number of initial adoption roadblocks such as legacy infrastructure, skill gaps, testing and validation requirements, security concerns and vendor lock-in.
Recent deployments
Telecom Egypt has announced its collaboration with the International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) to adopt intelligent automation technologies, aiming to implement an umbrella solution for all its operations support systems on mobile, fixed and core networks. The operator has adopted the IBM Cloud Pak for Watson AIOps and implemented IBM robotic process automation solutions. These solutions are expected to offer Telecom Egypt a holistic view of its entire IT environment and accelerate its innovation, reduce operational costs and minimise the time required to troubleshoot and resolve network-related incidents. Meanwhile, Philippines-based Converge ICT Solutions Inc. recently announced that it is building a zero-touch network operations centre (NOC). The company is initiating a process of end-to-end automation for the entire operational life cycle through its platform called the Network Intelligence and Automation Platform, which effectively integrates AI and automation into the operator’s network operations, encompassing functions such as monitoring, maintenance, trouble ticketing and resolution.
Tech Mahindra has partnered with Telefónica Germany to enhance the efficiency of network operations through the implementation of netOps.ai, a next-gen network automation platform that automates end-to-end network life cycle. The continuous insights and intelligence framework of netOps.ai has helped automate NOC operations, resulting in significant improvements in operational key performance indicators such as time to despatch, mean time to repair and network availability.
In 2022, Saudi Telecommunication Company (STC) deployed Ericsson’s AI-powered cognitive software solutions to boost user experience and network performance. The cognitive software uses automation and big data scalability to enhance network optimisation. It also proactively analyses the radio access network (RAN) of 4G and 5G networks. In addition, STC implemented 5G AI root-cause analysis to deliver an advanced 5G experience to its subscribers. Meanwhile, Libya Telecom and Technology (LTT) signed an agreement with P.I. Works, Inc. to implement the P.I. Works EXA automation solution across its national RAN. According to LTT, the solution will significantly improve its networks while lowering its opex and capex. South Africa-based MTN Group has signed an MoU with Rakuten Symphony to conduct live 4G and 5G open RAN PoC trials across South Africa, Nigeria and Liberia. These trials commenced in 2022 and are based on the Rakuten Communications Platform, which includes cloud orchestration, zero-touch provisioning and the automation of radio site commissioning and network integration.
 Earlier, Japan-based Kokusai Denshin Denwa Corporation selected Nokia’s 5G core and converged charging software, facilitating its transition towards a fully automated, cloud-native 5G core architecture. According to Nokia, its cloud-native 5G core’s near-zero-touch automation capabilities would help the operator in achieving greater scale and reliability, resulting in reduced latency, increased bandwidth and higher capacity. Belgium-based Telenet has extended its managed services partnership with Ericsson. The deal will allow Ericsson to deploy the latest automation, AI and ML technologies to enhance the telco’s mobile and fixed network performance, ultimately providing an enhanced customer experience.
Earlier, Japan-based Kokusai Denshin Denwa Corporation selected Nokia’s 5G core and converged charging software, facilitating its transition towards a fully automated, cloud-native 5G core architecture. According to Nokia, its cloud-native 5G core’s near-zero-touch automation capabilities would help the operator in achieving greater scale and reliability, resulting in reduced latency, increased bandwidth and higher capacity. Belgium-based Telenet has extended its managed services partnership with Ericsson. The deal will allow Ericsson to deploy the latest automation, AI and ML technologies to enhance the telco’s mobile and fixed network performance, ultimately providing an enhanced customer experience.
Given the escalating cost of electricity, it is logical that operators are employing AI to optimise power consumption in their networks. Telefónica Spain was the first operator to test the energy-saving functionality of the deep sleep mode at a 5G-deployed site. Through the integration of AI/ML solutions, the company achieved savings of up to 8 per cent during the site’s total 24-hour consumption, and up to 26 per cent during low-traffic hours.
The way forward
New-age intelligent automation is steadily picking up pace as CSPs recognise its long-term operational and financial benefits. As with any other transformative technology, there are challenges that must be addressed during the initial phase of adoption. As technologies continue to evolve, companies will increase their investments in network automation to stay competitive and cater to the growing demands of modern telecom. Going forward, careful planning, a strategic approach to implementation and industry collaborations will be key to achieving large-scale automation of telecom networks.




